Porsche 928: Why Won't My Car Start?
Whether your car cranks continuously, or will not crank at all, this article provides a step-by-step procedure to determine what is keeping your 928 from starting.
This article applies to the Porsche 928 (1979-1995).
There are several essential components that are necessary for any engine to run. This includes fuel, spark (ignition), and compression. If any one of these three are missing, your Porsche 928 will fail to start. Additionally, if your battery is dead, or your starter has gone bad, you will not be able to crank the engine over to get it to run. The 928 can suffer from any one of these problems and can leave its owner hunting for the problem. Fortunately, there are a few common components that fail on the 928 but are easily fixed. The materials needed will vary depending on the potential use.
Materials Needed
- Battery booster pack or battery charger
- Metric combination wrench set
- Test light/Noid light
- Remote starter wires
- Ratchet with metric sockets
- Floor jack & jack stands
- Shop rags
- Digital multimeter
Step 1 – Check battery
If your 928 does not crank at all when you attempt to start the car, it is likely an issue with the battery. With the key in the "ON" position, you can read the battery voltage on the dash instrument cluster. A normal reading for a healthy battery should show just about 12 volts on the gauge. Anything less than 12 volts indicates the battery voltage is low, and the red light warning light on the voltage gauge will illuminate. Additionally, if the instrument cluster is completely dead and does nothing with the key on, the battery is dead. Inspect the connections at the battery to ensure the leads are making good contact. If leads are securely fastened, but you still have no power to crank then engine, test the battery and recharge or replace if necessary.
Related Articles
- Porsche 928: How to Jump-Start Your Car - Rennlist.com
- Porsche 928: How to Replace Battery - Rennlist.com
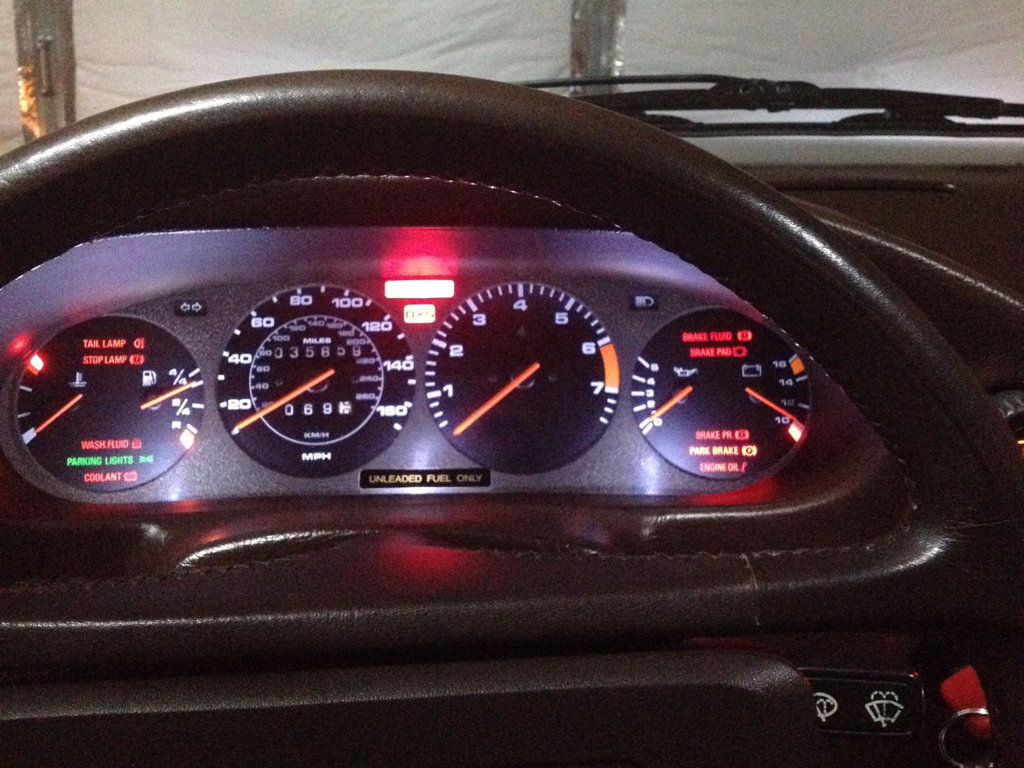

Figure 1. Dash gauge indicating low battery voltage.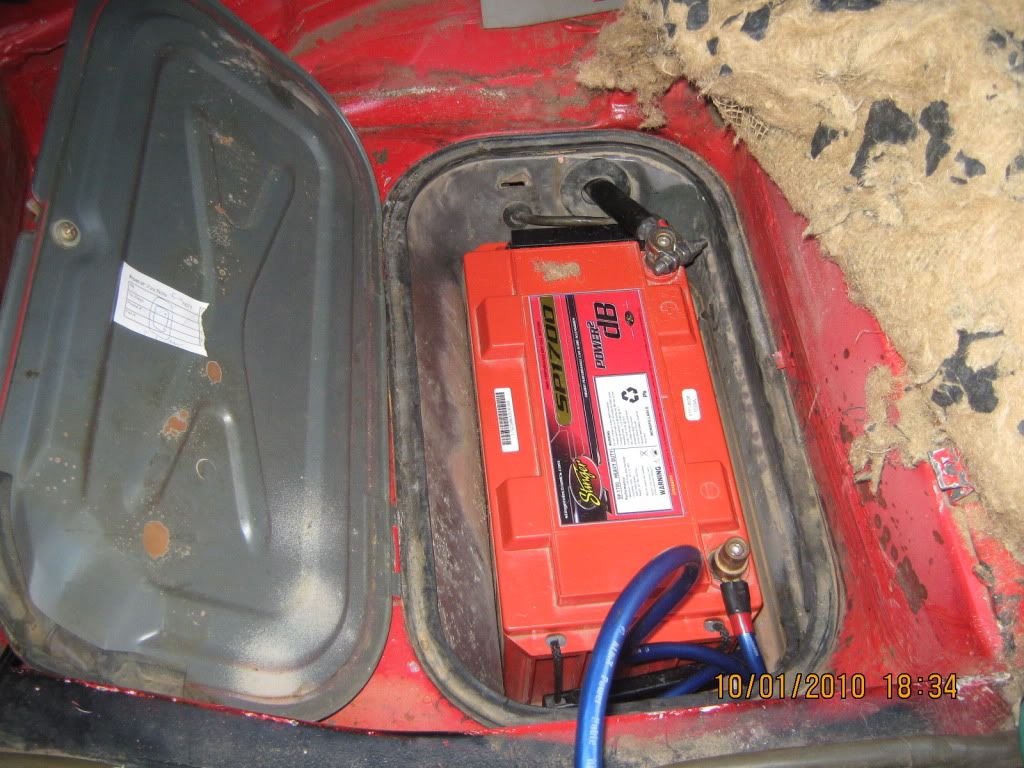 
Figure 2. Battery in rear hatch compartment.
Pro Tip
If you do not have access to a battery tester or multimeter to check the battery, any local auto parts store will typically test it for free.
If the battery is in good condition and is fully charged, proceed to Step 2.
Step 2 – Check starter and solenoid
If you your battery is in good condition and is fully charged but your 928 will still not crank, the starter solenoid is not being energized. The starter circuit includes the ignition switch, starter relay, starter solenoid, and wiring between these devices. Several tests can be done to determine the source of the problem.
- While turning the key to the "START" position, lift upwards on the key. If this allows the engine to crank, the problem is a worn out ignition switch which should be replaced.
- If the engine will still not crank, locate the fuse panel and swap the horn relay with the starter relay. These relays are interchangeable as they are the same part numbers. If the engine cranks with the horn relay in place of the starter relay, the starter relay should be replaced.
- If the starter will still not operate, slide under the car and use a remote starter switch or jumper wire to supply 12 volts to the starter solenoid by connecting one lead to the large red battery cable and the other to the small lead of the solenoid. Make sure the transmission is in neutral or park before attempting! If the starter engages and cranks the engine, faulty wiring to the starter is likely the cause. If the engine does not crank, the starter solenoid is the culprit and should be replaced.

Figure 3. 928 fuse panel, varies by model. 
Figure 4. Starter solenoid connections for testing.
If your engine cranks over fine, but will not start, proceed to Step 3.
Step 3 – Check fuel system
If you are not having any success starting your car, but the engine cranks over fine, a fueling problem may be present. If fuel is not able to freely make its way from the fuel tank to the fuel injectors at the engine, the car will not run. There are several components of the fuel system that can be inspected to ensure fuel is getting to the engine.
- The simplest way to see if the fuel injectors are putting fuel into the cylinders is to crank the engine over several times and then check a spark plug or two. If they are moist with fuel, the car likely has a fault in the ignition system.
- If there is no fuel on the spark plugs, you can simply crack a fuel line near the injectors open and have a friend crank the engine to see if fuel is present. If no fuel is there, it is likely the fuel pump, fuel pump relay, or fuel filter. If fuel is getting to the injector rails, it is likely a problem with the injectors or injection module. On 1985+ models with Lh-jetronic fuel injection, the fuel injection module has been known to fail. You can determine this by simply listening to the injectors while a helper turns the key to the on position. If the injectors are heard to be clicking, the fuel injection module has failed.
- To check the fuel pump relay, have a friend crank the car and listen for the fuel pump to whine. If it whines while cranking, it is most likely a bad fuel pump relay not allowing enough power to operate the fuel pump. This is a very common issue for a no-start condition on the 928. Replace the relay in the fuse panel.
- Inspect the fuel pump and fuel filter at the rear of the car. Both of these are regular service items that can fail and not allow fuel to the engine.


(Related Article: Porsche 928: How to Replace Fuel Pump & Filter - Rennlist.com)

Pro Tip
The fuel injector pulses can be tested with a noid light or test light to determine their operation.
If fuel is making its way into the cylinders, proceed to Step 4.
Step 4 – Check ignition system
If you have made it this far, the engine is cranking and you have good fueling, so the issue is likely with the ignition system. There must be spark in the cylinders to ignite the air/fuel mixture. If spark is absent, combustion will not occur and the engine will not run. There are several components that may be causing the issue.
- Inspect spark plug for spark. This can easily be done by removing a spark plug and spark plug wire from the engine and cranking the engine over. With the spark plug installed in the boot of the wire, look for spark at the spark plug.
- If there is no spark present, check the distributor cap and rotor. These are wear items with maintenance intervals that can keep the car from starting.
- If distributor cap and rotor are in good condition, inspect the ignition coil. Coil failure is not uncommon and will create a no-spark condition.
- Check crank position sensor (Lh-jetronic cars). The crank position sensor tells the computer when to fire the spark plugs. If the sensor is bad, it results in a no-spark condition. An easy test is to crank the engine and watch the tachometer. If it does not bounce and reads 0, the crank position sensor is bad. This is a rather common problem on later model 928's.
- Inspect green wire running from distributor (78-84 cars without Lh-jetronic injection). This wire sends the spark signal to the TSZ ignition control unit. A bad wire will result in no spark.
- Check EZK Ignition relay in fuse panel next to ECU. If bad, the "brains" of the ignition system will not operate correctly, thus giving a no-spark condition (Lh-jetronic cars only).
.jpg)
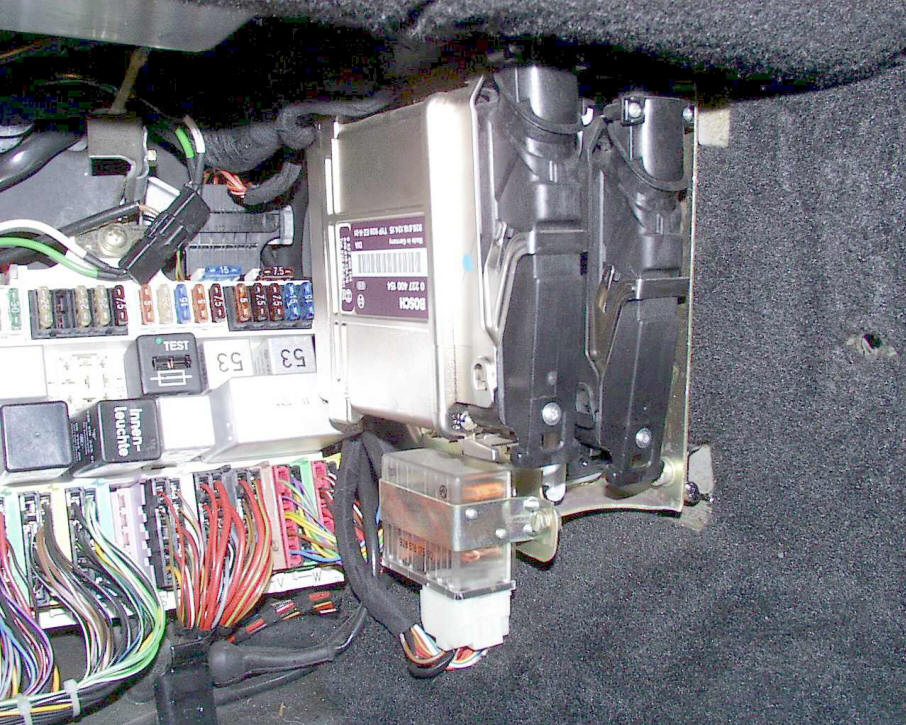

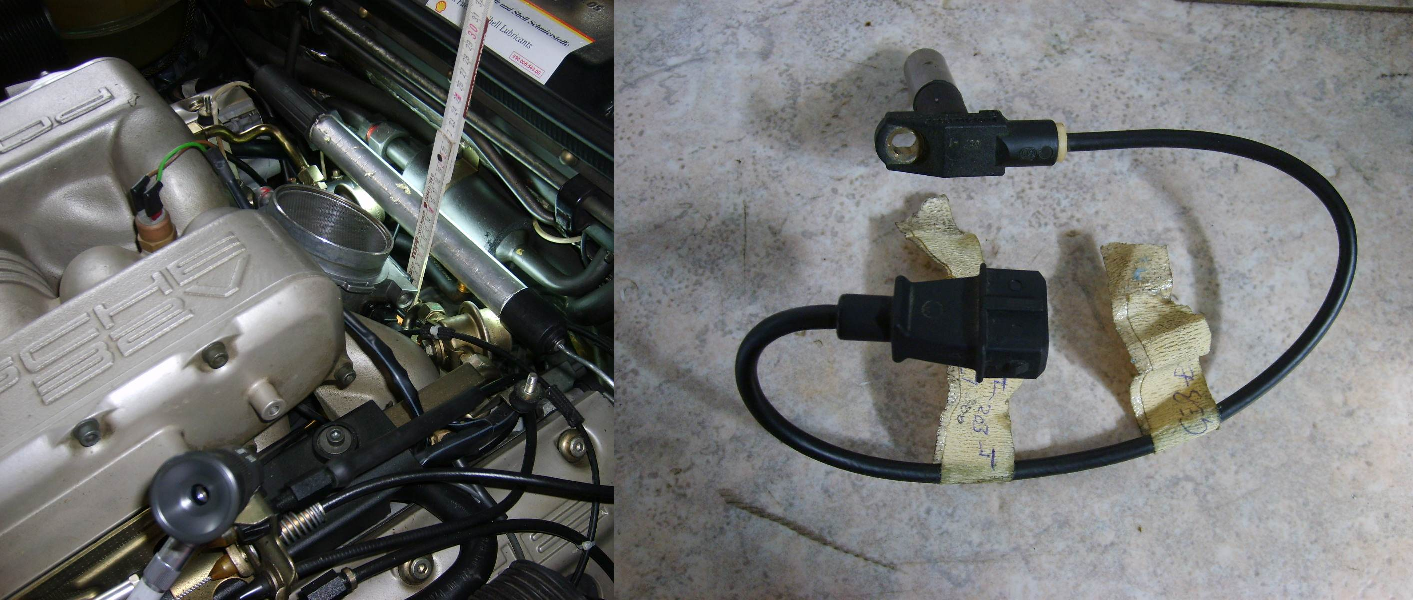

If you have fuel and ignition, proceed to Step 5.
Step 5 – Check timing belt and compression
If all else fails in an attempt to start your 928, check for timing belt failure. The factory-recommended replacement of the timing belt is 60,000 miles or every four years. This important belt can often go unserviced and has the potential to fail. If the timing belt breaks, the camshafts will not turn, thus not allowing the intake and exhaust valves to open. Without the valvetrain operating, the engine cannot run for lack of compression in the cylinders. As an alternative to inspecting the timing belt, you can simply do a compression test on each cylinder through the spark plug hole. If you are unfortunate enough to have no compression, you are looking at internal engine component damage that will require an engine rebuild.
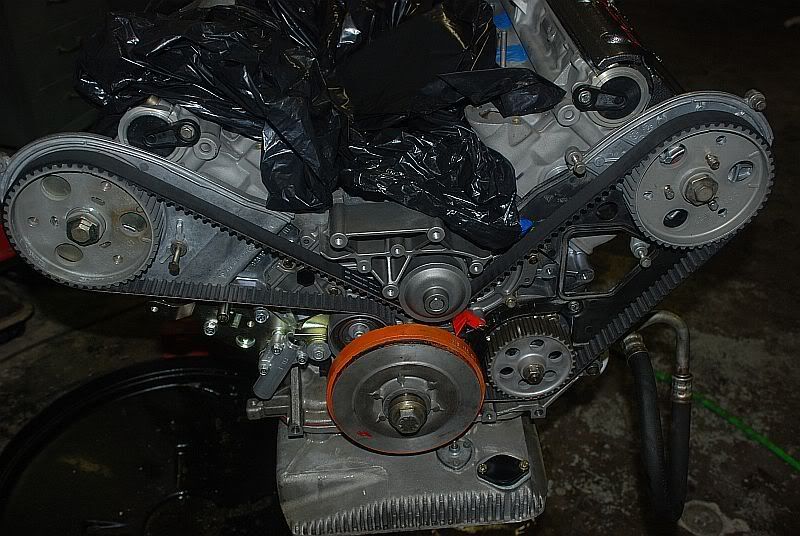

Figure 12. 928 Timing belt.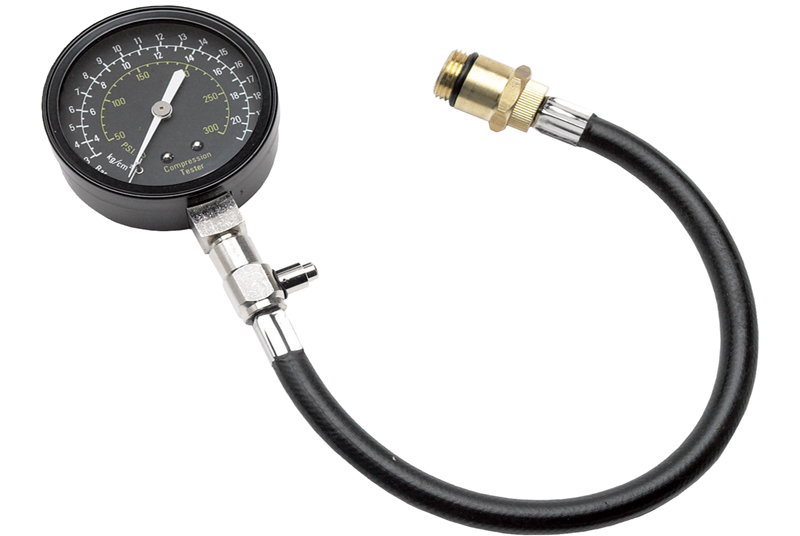 
Figure 13. Compression tester.
Related Discussions
- 928 S4 Doesn't Start - Rennlist.com
- 928 No Spark- Rennlist.com
- 928 S4 Cranks but Won't Start- Rennlist.com






